Chevrolet Cruze Repair Manual: Metric Fasteners
This vehicle provides fastener dimensions using the metric system. Most metric fasteners are approximate in diameter to equivalent English fasteners. Make replacements using fasteners of the same nominal diameter, thread pitch, and strength.
A number marking identifies the OE metric fasteners except cross-recess head screws. The number also indicates the strength of the fastener material. A Posidrive® or Type 1A cross-recess identifies a metric cross-recess screw. For best results, use a Type 1A cross-recess screwdriver, or equivalent, in Posidrive® recess head screws.
GM Engineering Standards and North American Industries have adopted a portion of the ISO-defined standard metric fastener sizes. The purpose was to reduce the number of fastener sizes used while retaining the best thread qualities in each thread size. For example, the metric M6.0 X 1 screw, with nearly the same diameter and 25.4 threads per inch replaced the English 1/4-20 and 1/4-28 screws. The thread pitch is midway between the English coarse and fine thread pitches.
Fastener Strength Identification
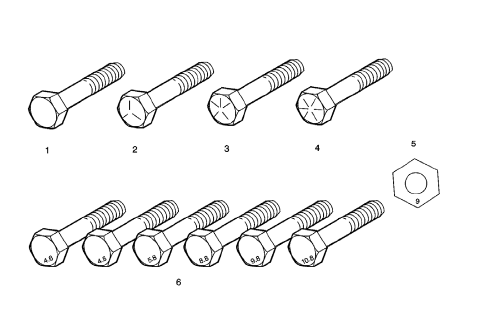
- English Bolt, Grade 2 (Strength Class)
- English Bolt, Grade 5 (Strength Class)
- English Bolt, Grade 7 (Strength Class)
- English Bolt, Grade 8 (Strength Class)
- Metric Nut, Strength Class 9
- Metric Bolts, Strength Class Increases as Numbers Increase
The most commonly used metric fastener strength property classes are 9.8 and 10.9. The class identification is embossed on the head of each bolt. The English, inch strength classes range from grade 2 to grade 8. Radial lines are embossed on the head of each bolt in order to identify the strength class. The number of lines on the head of the bolt is 2 lines less than the actual grade. For example, a grade 8 bolt will have 6 radial lines on the bolt head. Some metric nuts are marked with a single digit strength identification number on the nut face.
The correct fasteners are available through GM SPO. Many metric fasteners available in the aftermarket parts channels are designed to metric standards of countries other than the United States, and may exhibit the following:
- Lower strength
- No numbered head marking system
- Wrong thread pitch
The metric fasteners on GM products are designed to new, international standards. The following are the common sizes and pitches, except for special applications:
- M6.0 X 1
- M8 X 1.25
- M10 X 1.5
- M12 X 1.75
- M14 X 2.00
- M16 X 2.00
 Fasteners
Fasteners
Table 1: Metric Prevailing Torque Fastener Minimum Torque Development
Table 2: English Prevailing Torque Fastener Minimum Torque Development ...
 Prevailing Torque Fasteners
Prevailing Torque Fasteners
Prevailing torque fasteners create a thread interface between the fastener
and the fastener counterpart in order to prevent the fastener
from loosening.
All Metal Prevailing Torque Fasteners
Thes ...
Other materials:
Filling the Tank
WARNING
Fuel vapors and fuel fires burn violently and can cause injury or death.
• To help avoid injuries to you and others, read and follow all the instructions
on the fuel pump island.
• Turn off the engine when refueling.
• Keep sparks, flames, and smoking materials away from fuel.
• Do no ...
Hazard Warning Flashers
(Hazard Warning Flasher):
Press and momentarily hold this button on the instrument panel above the climate
control system, to make the front and rear turn signal lamps flash on and off. This
warns others that you are having trouble.
Press and momentarily hold again to turn the flashers off ...
Wiper Blade Replacement
Windshield wiper blades should be inspected for wear and cracking.
Replacement blades come in different types and are removed in different ways.
Notice: Allowing the wiper arm to touch the windshield when no wiper
blade is installed could damage the windshield. Any damage that occurs would not
...
